目录
前言
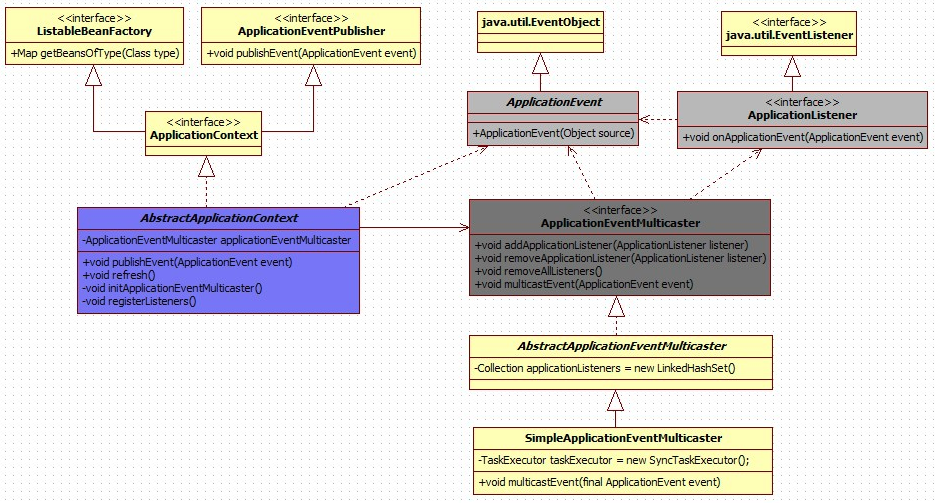
事件是 ApplicationContext 容器提供的一种能力,主要通过 ApplicationEvent 类和 ApplicationListener 接口实现。
如果一个实现了 ApplicationListener 接口的 bean部署到 ApplicationContext 容器中,那么每当 ApplicationEvent 事件发布到了容器,实现了 ApplicationListener 接口的 bean 就会被通知。
事件的分类
事件有两种:一种是标准事件,另一种是自定义事件。
标准事件
标准事件是Spring默认提供的,有下面几个:
-
ContextRefreshedEvent在初始化或刷新ApplicationContext时发布 -
ContextStartedEvent在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上使用start()方法启动ApplicationContext时发布。 -
ContextStoppedEvent在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上使用stop()方法停止ApplicationContext时发布。 -
ContextClosedEvent当使用ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上的close()方法或通过 JVM shutdown hook 关闭ApplicationContext时发布。 -
RequestHandledEvent每当一个HTTP请求完成后,会发布此事件。 -
ServletRequestHandledEventRequestHandledEvent的一个子类,用于添加 Servlet 特定的上下文信息。
自定义事件
可以通过继承 ApplicationEvent 类实现自定义的事件。
public class BlockedListEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private final String address;
private final String content;
public BlockedListEvent(Object source, String address, String content) {
super(source);
this.address = address;
this.content = content;
}
// accessor and other method...
}
但从 Spring 4.2 开始,Spring 的事件架构显著改善,提供了基于注解的模型以及发布任意事件的能力。也就是说,不需要继承 ApplicationEvent 的对象也可以作为一个事件发布,Spring 会帮你把这个对象包装到一个事件中。(包装成了PayloadApplicationEvent 事件)
事件的发布
通过 ApplicationEventPublisher 接口的 publishEvent() 方法发布自定义的 ApplicationEvent 事件。
@Component
public class EmailService implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
private List<String> blockedList;
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public void setBlockedList(List<String> blockedList) {
this.blockedList = blockedList;
}
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public void sendEmail(String address, String content) {
if (blockedList.contains(address)) {
publisher.publishEvent(new BlockedListEvent(this, address, content));
return;
}
// send email...
}
}
监听器的实现
方式一
实现 ApplicationListener 接口定义监听器,重写 onApplicationEvent 方法实现处理监听逻辑。
@Component
public class BlockedListNotifier implements ApplicationListener<BlockedListEvent> {
private String notificationAddress;
public void setNotificationAddress(String notificationAddress) {
this.notificationAddress = notificationAddress;
}
public void onApplicationEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...
}
}
事件监听器可以注册很多个,但默认情况下,接收到的事件是同步进行处理的。也就是说,publishEvent() 方法会阻塞,直到所有监听器都完成对事件的处理才能继续发布。
这种方法只能监听继承了 ApplicationEvent 类实现的自定义事件。
方式二
方式二是基于注解的。监听器的写法更简单了,只需要在监听事件的方法签名上添加一个注解 @EventListener 即可,不需要再实现 ApplicationListener 接口。
@Component
public class BlockedListNotifier {
private String notificationAddress;
public void setNotificationAddress(String notificationAddress) {
this.notificationAddress = notificationAddress;
}
@EventListener
public void processBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...
}
}
一些细节点
@EventListener 注解的进一步使用
1、使用 classes 属性监听多个事件或定义无参方法
如果需要同一个监听器监听多个不同的事件或者使用无参的方法签名,可以直接将事件写在注解上
```java
@EventListener(classes = {ContextStartedEvent.class, ContextRefreshedEvent.class})
public void handleContextStart() {
// ...
}
```
2、使用 condition 属性结合 SpEL(Spring Expression Language) 表达式添加对事件属性的过滤条件,更细粒度的控制需要处理满足指定条件的事件
```java
// 监听器执行的条件:当 BlockedListEvent 对象中的 content 属性值为 my-event 时
@EventListener(condition = "#blEvent.content == 'my-event'")
public void processBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent blEvent) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...
}
// 监听器执行的条件:当 ServletRequestHandledEvent 的 requestUrl 属性值匹配 /public/hr/.* 时
@EventListener(condition = "#event.requestUrl.matches('/public/hr/.*')")
public void onApplicationEvent(ServletRequestHandledEvent event) {
// 执行具体处理逻辑
}
```
监听器方法也可以有方法返回值
在处理完一个事件后,可以通过方法返回值的方式发布另一个事件或一组事件
// 发布另一个事件
@EventListener
public ListUpdateEvent handleBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress and
// then publish a ListUpdateEvent...
}
// 发布一组事件
@EventListener
public List<ListUpdateEvent> handleBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress
// publish multiple ListUpdateEvent
List<ListUpdateEvent> events = new ArrayList<>();
events.add(new ListUpdateEvent(..));
events.add(new ListUpdateEvent(..));
events.add(new ListUpdateEvent(..));
return events;
}
注意⚠️:异步监听器不支持这个特性。
异步监听器
如果需要异步执行监听器,那么可以通过在监听器上面添加一个 **`@Async`** 注解实现。
```java
@EventListener
@Async
public void processBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// BlockedListEvent is processed in a separate thread
}
```
注意的点⚠️:
- 如果一个异步事件监听器抛出了异常,这个异常不会传播给调用方。
- 异步事件监听器方法无法通过返回值来发布后续事件。但可以通过手动注入 **`ApplicationEventPublisher`** 来发布后续事件。
通过 @Order 注解可以指定监听器执行顺序
// 值越小优先级越高
@EventListener
@Order(42)
public void processBlockedListEvent(BlockedListEvent event) {
// notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...
}
总结
通过了解以上的知识,相信已经足够在项目开发中使用Spring Event来完成一些需求了。